创建连续对话
在一些使用场景里,需要机器人与使用者产生连续的对话。比如询问使用者以获取信息等。
Message 对象内置了连续对话支持。
Message.wait()
参数列表
| 参数名 | 类型 | 释义 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| reply | Chain | Chain 对象 | |
| force | bool | 使用强制等待 | False |
| max_time | int | 最长等待时间(秒数) | 30 |
| data_filter | Callable | Message 过滤器 | |
| level | int | 优先级 | 0 |
使用 wait 方法实现一个简单的连续对话
@bot.on_message(keywords='hello')
async def _(data: Message):
reply = await data.wait(Chain(data).text('tell me your name please~'))
if reply:
return Chain(reply).text(f'hello,{reply.text}')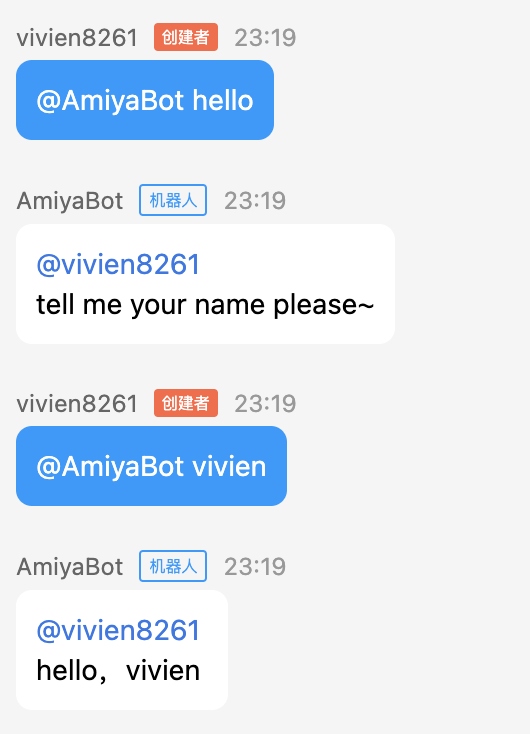
force 强制等待
等待通常不会影响消息分配器运作,也就是说 仅在不能触发任何其他功能 的时候,消息才会返回到当前等待处。(也包括本功能的初始触发方式,一般功能的优先级默认为 1,比等待事件的默认优先级高)
如果你不希望如此,使用参数 force=True,可以忽略分配器让消息强制返回到等待处。
data_filter 消息过滤器
如果在等待过程中,希望 wait 接收到符合期望的消息后再返回到等待处,可以使用 data_filter 参数过滤消息。
async def my_data_filter(data: Message):
if ...:
return True # 返回 True 代表此则消息符合期望,将返回到等待处
@bot.on_message(keywords='hello')
async def _(data: Message):
reply = await data.wait(Chain(data).text('tell me your name please~'), data_filter=my_data_filter)
if reply:
return Chain(reply).text(f'hello,{reply.text}')关于 wait 方法你需要知道的事
- 若用户超过最长等待时间未回复,wait 会返回
None。
同一个子频道内的同一个用户只能存在一个等待事件,当一个新的等待事件创建后,上一个未使用的等待事件会被注销并引发 WaitEventCancel 异常,进行中的业务将会被终止,这是符合预期的,通常这个异常会被全局异常捕捉器过滤。
- 在等待时间内使用其他功能,等待也会被注销。
Message.wait_channel()
注意
该方法不可用于支持私信的功能里
参数列表
| 参数名 | 类型 | 释义 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| reply | Chain | Chain 对象 | |
| force | bool | 使用强制等待 | False |
| clean | bool | 是否清空消息列表 | True |
| max_time | int | 最长等待时间(秒数) | 30 |
| data_filter | Callable | Message 过滤器 | |
| level | int | 优先级 | 0 |
wait_channel 方法用于等待子频道全体成员的回复。
与 wait 方法不同的是,wait_channel 返回的不是 Message 对象,而是 ChannelMessagesItem 对象。内含等待事件的实例,和该次返回的消息。
ChannelMessagesItem
属性
| 属性 | 类型 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|
| event | ChannelWaitEvent | 等待事件的实例 |
| message | Message | Message对象 |
方法
| 方法名 | 参数 | 释义 | 异步 |
|---|---|---|---|
| close_event | 关闭等待事件 | 否 |
下面来看一个简单的例子
@bot.on_message(keywords='hello')
async def _(data: Message):
await data.send(Chain(data).text('hello everyone, tell me your name please~'))
while True:
await asyncio.sleep(0)
event = await data.wait_channel()
if event:
reply = event.message
if reply.text == 'stop':
event.close_event() # 关闭等待事件
break
await data.send(Chain(reply).text(f'hello,{reply.text}'))close_event()
关闭等待事件
wait_channel 与 wait 的用法是大致相同的,但是 wait_channel 在接收到有效消息并返回后,不会像 wait 那样关闭事件,而是保持接收子频道的消息。在你的业务逻辑正常结束时,你必须使用 close_event 关闭它。
请注意
请务必让你的业务逻辑有机会关闭等待事件,否则等待事件没有被正常关闭时,它可能会持续拦截子频道消息直至超时自动关闭。
不清除消息队列
如果你持续调用 wait_channel(如示例所示),但你不希望在处理业务时错过子频道内的消息,可以设置参数 clean=False 让事件不清除消息队列。让你可以按顺序获取到子频道内的消息。
await data.wait_channel(clean=False)